Activation Steering for Discrete Language Diffusion Models
Project Background
Diffusion models have recently emerged as a powerful paradigm for generative modeling, achieving state-of-the-art results in continuous domains such as images and audio. In the discrete domain, masked language diffusion models aim to generate coherent sequences of tokens through iterative denoising steps, offering a compelling alternative to autoregressive models.
Despite their promise, discrete language diffusion models face several challenges:
- Mode collapse or repetitive token sequences
- Lack of controllability over style, tone, or semantic traits
- Sensitivity to sampling strategies
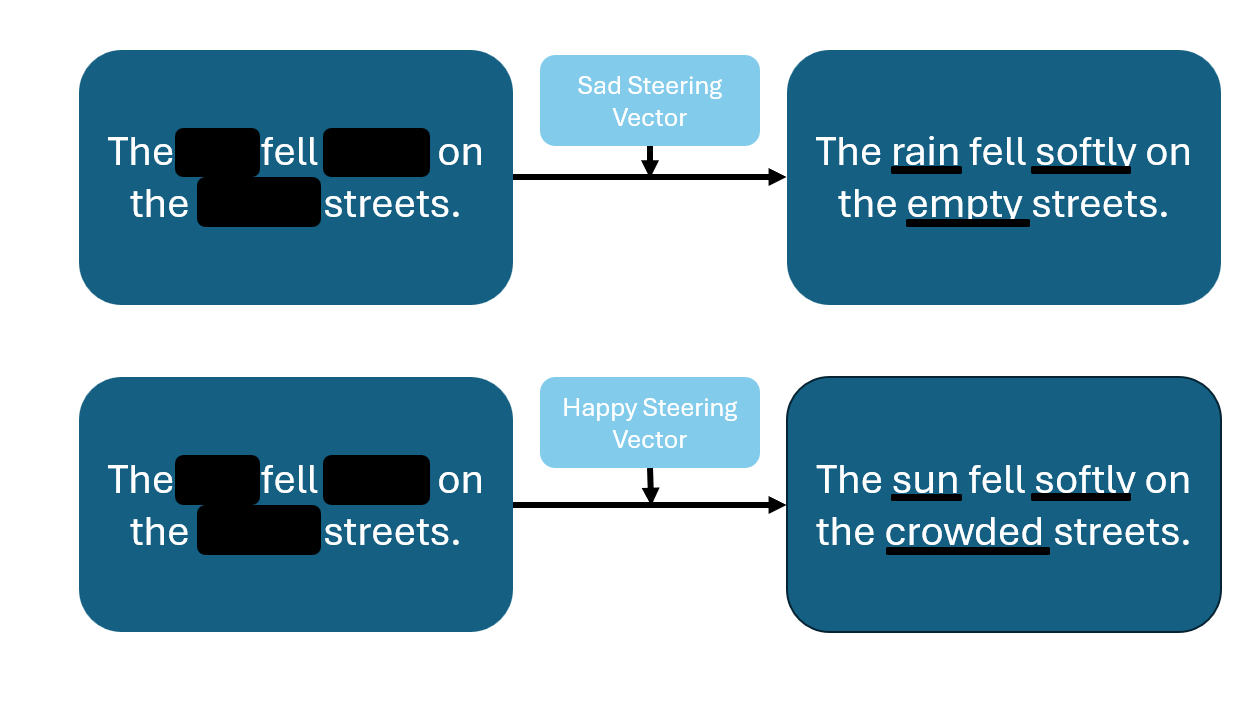
Activation steering, which has shown success in transformers for controlling textual traits post-training, could provide a novel mechanism to guide discrete diffusion processes. By identifying directions in the model’s hidden activations corresponding to specific traits (e.g., formality, sentiment, or domain-specific style), it is possible to modulate generated sequences without retraining the model.
Applying activation steering to discrete language diffusion models could allow for more controllable, coherent, and high-quality text generation, making this a promising avenue for research. Extending on the fine grained control: Applying activation steering to masked language diffusion models allows to steer only selected tokens allowing for a fine grained level of control not acchievable with decoder only LLMs.
Your Tasks
- Literature Review: Survey discrete language diffusion methods, activation steering techniques, and related controllable generation approaches.
- Experimental Design: Develop evaluation frameworks for measuring control, coherence, and quality of text generated under activation steering.
- Steering Vector Extraction: Implement methods to identify activation directions corresponding to semantic or stylistic traits in diffusion models and evaluate the superposition of these sterring vectors.
- Evaluation: Benchmark performance using automatic metrics (perplexity, BLEU, diversity) and human evaluation to assess controllability and fluency.
What We Offer
- Opportunity to work on a cutting-edge generative AI project with publication potential.
- Freedom to explore novel applications of activation steering in discrete generative models.
- Close supervision and collaboration opportunities with experts in NLP and machine learning.
- Access to computational resources including:
- A dedicated cluster with multiple A40 and A100 GPUs
- Fast SSD-backed storage
- Tools for efficient experiment management
Project Details
Duration: 6 months
Required Background:
- Strong programming skills (Python/PyTorch)
- Solid understanding of machine learning fundamentals
- Interest in generative models and NLP
- (Preferred) Experience with transformers, diffusion models, or controllable text generation
- Ability to work independently and collaboratively in interdisciplinary teams
How to Apply
Please send a short motivation statement, your CV, and a recent transcript of records to:
johannes.kaiser@tum.de
References
- Lou, Aaron, Chenlin Meng, and Stefano Ermon. “Discrete diffusion modeling by estimating the ratios of the data distribution.” https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.16834 (2024).
- Chen, R. et al. Persona Vectors: Monitoring and Controlling Character Traits in Language Models. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2507.21509 (2025).
- Rimsky, N. et al. Steering Llama 2 via Contrastive Activation Addition. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/html/2312.06681v2 (2023).
- Anthropic Blog Post: Evaluating Feature Steering