Activation Steering for Robust Multi-Persona Report Generation
Project Background
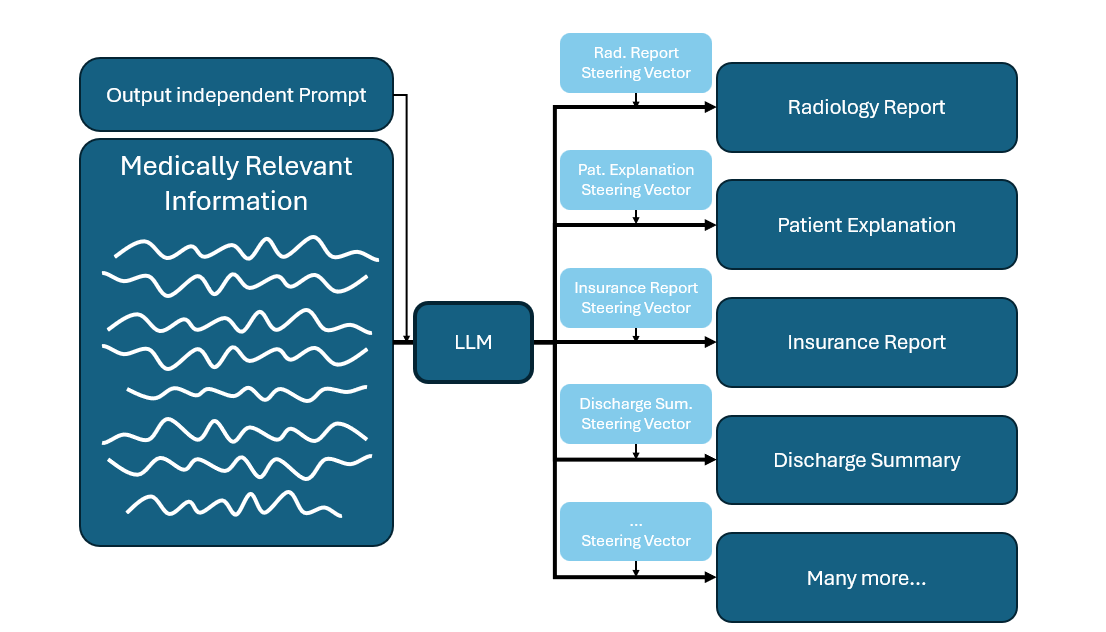
Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in medical contexts, ranging from diagnostic assistance to patient communication. In clinical practice, many different types of documents are generated based on patient examinations and subsequent diagnoses. These include, but are not limited to:
- Radiology reports
- Patient explanations
- Insurance reports
- Discharge summaries
- many more…
It is of utmost importance that these documents are coherent, medically sound, and consistent in their reasoning.
However, due to the probabilistic nature of next-token prediction in LLMs and the strong influence of prompts, even when models are asked to generate different types of reports (often framed as personas) from the same knowledge base, their outputs can diverge significantly.
Activation steering may offer a powerful method to reduce this variability and improve consistency across generated reports. Recent work in mechanistic interpretability has shown that specific linear directions in transformer activations correspond to distinct behavioral traits. Since these traits exist orthogonally to downstream tasks, they can be adjusted without altering task performance.
In activation steering, model activations are augmented with precomputed steering vectors that influence the tone or style of the output.
For example, adding a “friendly” steering vector to an otherwise neutral response yields a friendlier result.
Crucially, this method works post-training, making it a low-cost alternative to fine-tuning.
This project aims to evaluate whether activation steering can generate more consistent and reliable medical reports than prompt-based methods.
Your Tasks
- Literature Review: Survey activation steering methods, applications (especially in the medical domain), and automatic report generation.
- Experimental Design: Develop evaluation frameworks to test the effectiveness of steering across different types of medical reports, focusing on content consistency.
- Steering Vector Extraction: Implement methods to identify activation patterns corresponding to medically relevant document styles.
- Evaluation: Use both LLMs-as-judges and human experts to benchmark report consistency, quality, and domain fit.
What We Offer
- Opportunity to contribute to an exciting and impactful medical AI project with the goal of publishing in a top-tier conference.
- Freedom to shape the direction of the research and take ownership of your work.
- Close supervision and collaboration opportunities with experts in computer vision and medicine.
- Access to powerful computational resources, including:
- A dedicated cluster with multiple A40 and A100 GPUs
- Fast SSD-backed storage
- Custom tools for efficient job scheduling and data handling
Project Details
Duration: 6 months
Required Background:
- Strong programming skills (Python/PyTorch)
- Solid understanding of machine learning fundamentals
- Interest in healthcare applications
- (Preferred) Experience with LLMs, transformer architectures, or AI safety research
- Ability to work both independently and collaboratively in interdisciplinary teams
- Motivation to explore the use of LLMs in clinical settings
How to Apply
Please send a short motivation statement, your CV, and a recent transcript of records to:
johannes.kaiser@tum.de
References
- Chen, R., Arditi, A., Sleight, H., Evans, O. & Lindsey, J. Persona Vectors: Monitoring and Controlling Character Traits in Language Models. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2507.21509 (2025).
- Code: https://github.com/safety-research/persona_vectors
- Rimsky, N. et al. Steering Llama 2 via Contrastive Activation Addition. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/html/2312.06681v2 (2023).
- Anthropic Blog Post: Evaluating Feature Steering