Rotation Equivariant ProtoPNets in Medicine
ReProtoPNet is a novel AI model specifically designed to enhance both the interpretability and rotation invariance of machine learning systems, particularly for crucial medical applications. This development addresses significant limitations of traditional AI, which often function as “black-box” systems, making their decision-making processes opaque and difficult for healthcare professionals to trust.
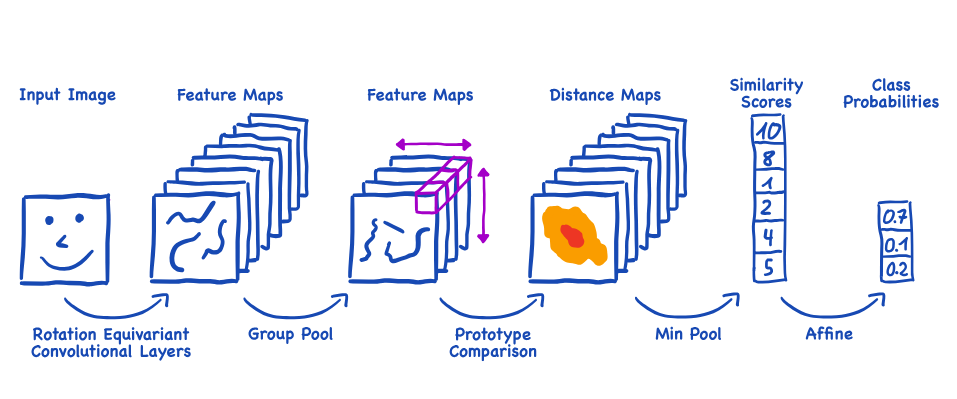
The foundation of ReProtoPNet is ProtoPNet, an existing Explainable AI (XAI) model that provides interpretability by classifying images based on their similarity to visually understandable “prototypes” or learned image patches.
However, a major challenge with the original ProtoPNet is its instability and inconsistency when input images are rotated; predictions can become unreliable, and reasoning may shift even with simple rotations, leading to inconsistent results.
To overcome this rotation sensitivity, ReProtoPNet integrates Group Equivariant Convolutional Neural Networks (G-CNNs), also known as Steerable Convolutional Neural Networks (Steerable-CNNs), into the ProtoPNet architecture.
The core principle of equivariance in G-CNNs ensures that if an input image is rotated, the internal feature representations within the network will also rotate in a corresponding and predictable manner. ReProtoPNet achieves this through rotation equivalent convolutional layers and a group pool operation that computes the minimum distance across all possible rotations for a prototype, ensuring that the prototype comparison is inherently rotation-invariant. An additional modification, Weight Down Corners (WDC), was also introduced to address potential artifacts and further improve interpretability, particularly when dealing with non-circular masks on distance maps.
Experiments on medical datasets demonstrate that ReProtoPNet significantly enhances prediction stability with respect to input rotations, leading to consistent reasoning across multiple rotations of the same image.
The model drastically reduces the variance of prototype distances and class probabilities for correctly classified samples compared to ProtoPNet. Specifically, ReProtoPNet achieved a variance roughly 300 times smaller, and with the WDC modification, this was further reduced to 500 times smaller variance, representing a 99.8% reduction. This advancement makes AI models more reliable and trustworthy for critical applications like medical diagnosis, where stable and consistent predictions are paramount.
